Today, we are interested in learning how mobile networks work to help us better understand, how communication is established technologically. Interestingly, one of this technology powering mobile networks are smartphones which can easily be described as a special kind of consumer electronics that plays a significant role in our day to day lifes.
It has no doubt evolved up to the point where it has become almost indispensible. Check the numbers and you are quick to find out that as of 2024 there are about 5.45 billion people connected to the internet across the globe. If you narrow this down, there are just around 4.88 billion smartphone users in 2024.
From internet connectivity to doing other basic stuffs like making calls, texting, playing games etc. You will agree with me that mobile phones have made it possible for you to stay connected on the go. But how does this technology work in the first place? Stay with me as I dive deeper to understand how mobile networks work.
Mobile Networks
A mobile network can be described as a communication system that makes use of a collection of cell towers otherwise called base stations to transmit radio signals, making it possible for mobile devices like smartphones to send and receive data, voice, and all forms of communication that exist within the network.
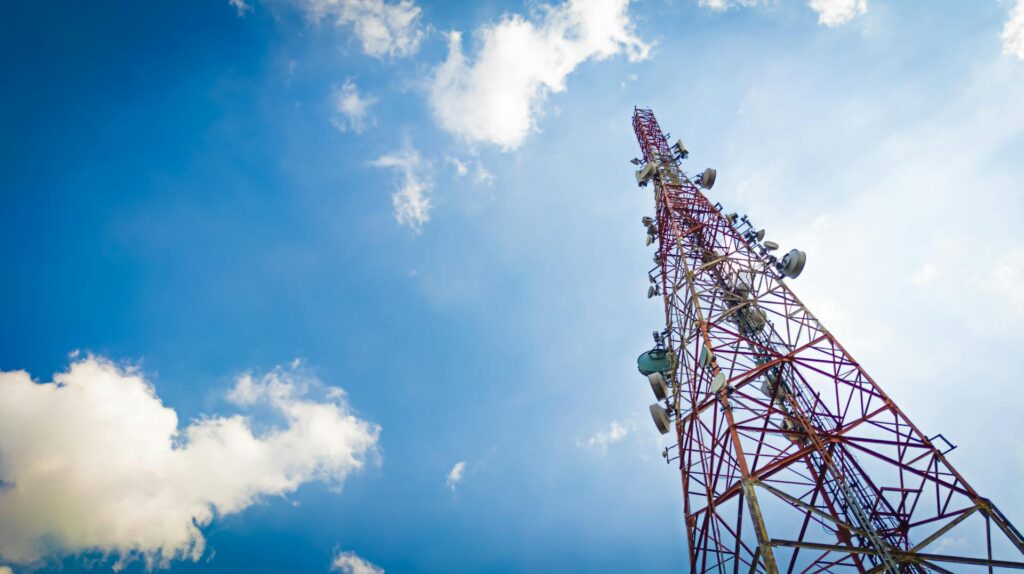

A Base Station
How mobile networks work here is by ensuring that this network infrastructure (e.g. base stations) help users stay automatically connected as they move from one cell (small geographical area) to another. These cells are typically hexagonal in design. By so doing, they help to minimize overlap or gaps between adjacent networks which to a very large extend helps to maximize coverage.
How Phone Signals Work in Cellular Networks
To better understand how mobile networks work, it is important to pay attention to the primary technology behind mobile networks called radio waves. These are used to transmit data between mobile devices and base stations. Anytime you make a call, send a text, or browse the internet, your mobile devices communicates with the nearest cell tower wirelessly using radio waves.
Here is a breakdown to better understand how this works:
- Device Registration: This is unarguably the first thing that happens when your phone is turned on. It begins by checking your SIM card for authentication to confirm your identity and allow access to the network. Next, it automatically scans for the closest base station it can find with the strongest signal and registers itself on the network.
- Data and Voice Transmission: The moment you decide to place a call or send data (e.g via browsing the internet), something happens under the hood. Your smartphone does a great job of converting the voice from call and data into digital signals which then gets transmitted as radio waves to the closest base station. The also happens the reverse as well.
- Base Station Communication: The base station handles communication by relaying signals coming from your phone to the core mobile network’s Mobile Switching Center (MSC). What the MSC does is that it route your call or data to the intended recipient which could be a smartphone or an internet server.
- Handover: The freedom to move from one place to another was carefully thought of too, hence the need for handover or handoff as some prefer to call it. Your phone will automatically switch from one base station to another as you move through different cells in the network. It works seamlessly that you don’t get to notice it at all. There are two types of handover:
- a)Hard Handover: Hard handover is said to have occurred when the current connection is broken before a new one is setup. This was very common in early generations of mobile networks like 2G.
- b)Soft Handover: In soft handover, the new connection is established first before the old one is broken; this ensures that there is no noticeable disruption in the network. Soft handovers are used in modern networks like 4G and 5G.
- Core Mobile Network and Data Routing: It is important to mention that the Mobile Switching Center spoken about earlier works alongside a Packet-Switched Network. Both are part of the core mobile network which is responsible for routing voice calls and managing data transmission. The core mobile network can also connect to external networks like the internet. Understood?
Cellular Network Architecture
Let’s go a little further to understand how mobile networks work by learning more about its architecture starting with its key components. The components of a typical cellular network are:
- Base Stations: Base stations, otherwise called Cell Towers have a primary role of transmitting signals between mobile devices and the network. Each base station is said to have limited coverage which is restricted to specific area called cell.
- Mobile Switching Center (MSC): Mobile Switching Center is considered the brain of the cellular network, this is because it does a great job of connecting phone calls, managing handovers, handling billing and security.
- Radio Frequencies: Mobile networks are designed to make use of specific bands of radio spectrum (a range of electromagnetic frequencies used for wireless communication) to transmit data. Different generations of mobile technology like 2G, 3G, 4G etc. use different frequency bands to improve speed and capacity.
- Backhaul Network: This is the connection that exists between the base stations and the core network. Backhaul can either be wired or wireless, ensuring that signals are relayed quickly and efficiently.
- Core Network: The core network is the central part of the network that connects mobile users to external networks and services like the internet , voice over IP, satellite communication systems etc.
Final Thoughts
The mobile networks you use today are complex combination of technology and infrastructure put together to ensure that there is seamless communication across the globe. Looking at the basic voice services offered by 2G to the present day ultra-fast speeds of 5G. mobile networks has continued to evolve while ensuring that we stay connected wherever we go.
We covered some fundamentals to understanding how mobile networks work, including how phone signals are transmitted, how base stations function, and the role of different network components to help us gain more insight into the invisible systems powering our mobile devices. Hope you found this useful, catch you on the next one. Bye!