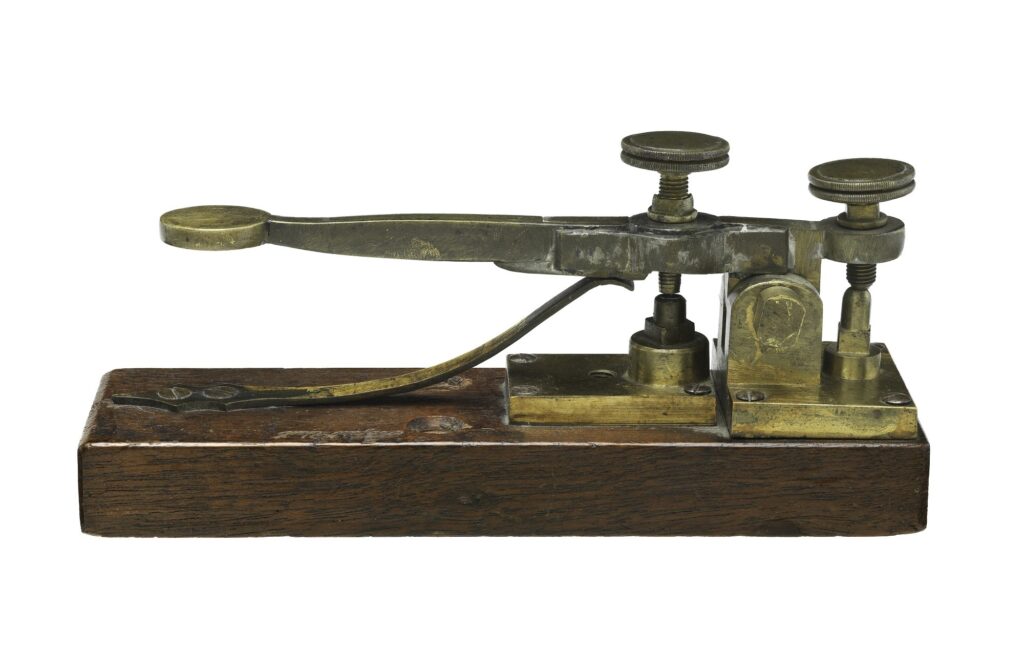
The Invention of Telegraph came at a time when long-distance method of communication available in the early 19th century where very slow and not reliable. Messages took day or months to deliver, civilization had gotten to the point where people needed some form of quick communication over long distance.
The discovery of electricity and magnetism spark some interest among scientist and inventors to the point where they began to wonder what kind of technology could come out of it. The Invention of Telegraph happened to be one of them, and it turned out to be one of the greatest inventions of the 19th century.
Early Attempts at long-distance messaging
What led to the invention of telegraph is said to have began in 1774 when a Swiss physicist called Georges-Louis Le Sage created an early version of the telegraph system which had 24 wires representing individual letter.
Next was the invention of an early kind of battery called voltaic pile by Alessandro Volta in 1800. This discovery proved that a reliable source of electric current exists. Further increasing the interest of others to dive deeper into the world of electricity.
In 1820, Hans Christian Ørsted while conducting an experiment on electricity found out that electric currents were capable of creating magnetic fields. This was mind blowing because it set new possibilities for communication technology which led to the Invention of Telegraph.
After this, several inventors across Europe kept on experimenting with the telegraph. Russian scientist Pavel Schilling built an electromagnetic telegraph that used a needle to point at distinct signs on a board in 1832.
On the other hand, Carl Friedrich Gauss and Wilhelm Weber in 1833 developed a telegraph system that could transmit messages using electromagnetic signals over one kilometre in Germany.
In Britain, a five-needle telegraph system was built by Sir Charles Wheatstone and Sir William Fothergill Cooke in 1837. This was innovative but appeared complex due to the fact that it requires several wires. However, Samuel Morse found out about this and began thinking of new ways to reinvent it.
The Telegraph that Transformed Communication
An American named Samuel Morse, born in 1791 began his career as an artist before later becoming an inventor. He is credited for discovering the telegraph that revolutionized long-distance communication. Motivated by the death of his wife due to slow communication over long distance, he was determined to find a faster way to communicate.
This happened when America was in daring need of a fast communication system over long-distances, making it a perfect time for Samuel Morse. He teamed up with Alfred Vail who happened to be a skilled machinist to develop the Morse code.

The Morse code is a simple and effective coding system that uses dots and dash to represent letters and numbers. This was crucial for the invention of telegraph as it later made room for easy adoption in not just America but across the world.
How was the Telegraph made?
The telegraph that Americans developed had a single wire as opposed to what was earlier invented by the British, making it more practicable and cost effective. The basic component comprises of a key that worked like a switch when pressed to send signals, a battery that generate the electrical power required for sending signals, a sounder or receiver that makes a clicking sound at the receiving end and lastly a physical copper wire that transmit the electric signal.
Sending the First Telegraph Message
In 1837, The Invention of Telegraph became a reality and Samuel Morse successfully sent the first message that read “What hath God wrought”. The sending of the first message worked by pressing the key in a specific order to enable him write the Morse code which then gets translated.
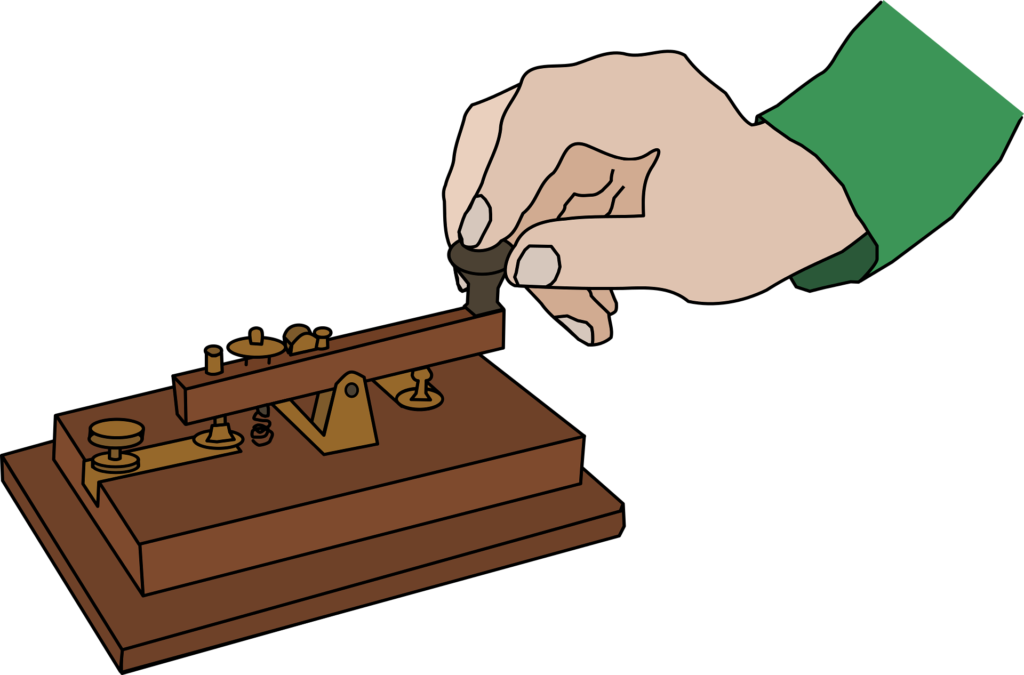
On the Technical side, each time a key is pressed by the sender; an electric pulse (signal) is generated which represent the dots and dashes in Morse code. At the same time, an electric circuit (path) is formed to allow electricity to flow immediately through the copper wire which then enables electric pulses (signal) to travel through the wire to the receiver’s end.
On the Receiver end, the incoming electric pulses (signal) made the sounder to click. For a dot, it clicked just once but holds longer for a dash. These series of clicks are then listened to carefully and written in Morse code which gets translated to letters and symbols.
Having made this work, Morse sought financial support from the U.S Congress in 1843 with the help of a congressman from Maine called Francis Ormand Jonathan Smith. The sum of $30,000 was granted to him, enabling him to construct an experimental line from Washington, D.C to Baltimore, Maryland.
Expansion
The Invention of the Telegraph in America was successful following the demonstration of the first telegraph message. Infrastructures followed suit which led to construction of a Telegraph lines across the United States of America. By 1861, the first transcontinental telegraph line that linked the east and west coasts was completed.

With instant communication becoming popular, many saw how beneficial it was and plans were being put in-place to connect North America and Europe. After several attempts, the first successful transatlantic telegraph cable was laid in 1866 making it possible for messages to be sent across continents in minutes. The American Telegraph was easily adopted outside of America because it was easier to use, simpler and more cost-effective.
Global Impact
The Invention of Telegraph disrupted a whole bunch of sectors. It was very evident that the way the world communicates was never going to be the same anymore. Let’s have a look at some of these sectors that underwent through these transformations:
Commerce
Business practices improved as a result of the fast communication that became possible through the invention of telegraph. Companies can now communicate more with each other to facilitate trade across long distances and the management of the financial market improved as well.
Military and Government
Telegraph was quickly adopted by the military and government to aid their ability to respond and manage their administration and other events in real-time.
Social Impact
The world began to feel like a global village, with distance places feeling closer. Telegraph helped to improve connectivity tremendously, enabling people and nations to understand each other better.
Journalism
The way and manner news were being sourced and reported changed. With communication happening quickly over long distances, the press had to meet up with this new invention that came through the Telegraph.
Other Technologies
The Invention of Telegraph also laid the foundation for the development of other inventions like the telephone, television and radio. They were built based on the concept of electrical communication that telegraph already had and were working excellently.
A Researcher and Software Engineer who is committed to bridging the digital divide in underserved communities.